What are Hip Ligament Injuries?
Injuries to the hip ligaments are commonly called a hip sprain and can range from minor tears of the ligaments to more serious injuries involving the hip muscles, tendons or bone.
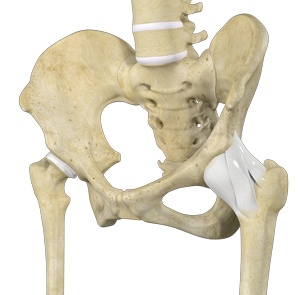
The hip joint is a ball and socket joint; the ball being the head of the femur (thigh bone) and the socket is the acetabulum of the pelvis. Tendons, muscles, and ligaments hold the joint in place.
The ligaments of the hip are:
- Iliofemoral Ligament: Attaches the femur to the pelvis at the front side
- Pubofemoral Ligament: Attaches the pubis (a pair of pelvic bones) to the femur
- Ischiofemoral Ligament: Attaches the femur to the pelvis at the lower end
Causes
Injuries to hip ligaments can occur due to:
- A trauma
- A blow or fall over the hip
- Over-stretching of the hip
Symptoms
You may hear a ‘pop’ sound at the time of injury. Other symptoms include:
- Pain and bruising around the hip
- Inability to bear weight on the affected hip joint
- Poor movement of the joint
Diagnosis
Your doctor will assess your symptoms and take your medical history. Specific movements of your hip may be performed. The exact location and severity of the pain are essential to identify the type and extent of the damage. Your doctor may order an X-ray, CT-scan or MRI to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
Your treatment plan includes:
- A combination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and opioids to manage pain.
- RICE method
- Rest: Avoid activities that may intensify pain and discomfort.
- Ice: Ice packs applied to the injury will help reduce swelling and pain. Ice should be applied over a towel to the affected area for 15-20 minutes, 4 times a day for several days. Never place ice directly on the skin.
- Compression: Wrapping with an elastic bandage can help minimise the swelling and support the hip.
- Elevation: Elevating your leg above heart level will also help reduce swelling and pain.
- Physiotherapy exercises to enhance your flexibility, range of motion and strength.
Surgery is recommended if you do not respond to non-surgical treatment options.
Prevention
Hip ligament injuries can be prevented by:
- Practising strengthening and stretching exercises regularly
- Avoiding rough surfaces and wearing proper shoes while running
- Avoiding participation in sports if any pain is experienced







